Table of Contents
What is NTFS File System?
The file system used by operating system Windows NT for the purpose of retrieving or storing files on the hard disk is termed as NTFS or New Technology File System. NTFS stands as Windows NT correspondent of OS/2 HPFS (High Performance File System) and Windows 95 FAT (file allocation table).
However, the number of improvements are offered by NTFS over HPFS and FAT in terms of extendibility, performance and security.
NTFS’s Features –
- Keeping track of file clusters with the use of the directory scheme of b-tree
- With each cluster, it stores the information regarding clusters of file and other data
- Incorporated file compression
- Large files support
- Support for Unicode based names
- An ACL (access control list) that gives the control to server administrator to decide as who could be given with the access of specific files
- Security of data on both fixed and removable disks
- Long file names support along with 8” by 3” names
Related Blog – NTFS vs FAT 32
NTFS Structure
Below structure shows the architecture of the NTFS file system –
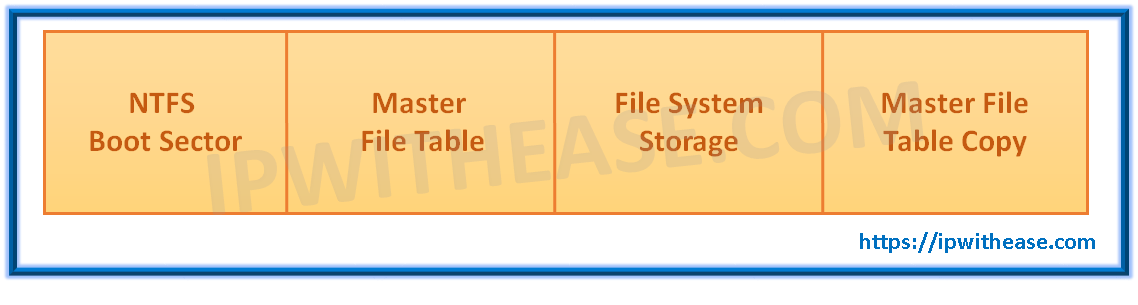
- NTFS Boot Sector – This portion contains the BIOS parameter block used to store information of volume layout and the file system structures, including the boot code that loads Windows Server 2003.
- Master File Table – This portion contains the essential information to retrieve files from the NTFS partition like file attributes etc.
- File System Data – This portion stores data that is not contained within the Master File Table.
- Master File Table Copy – This portion contains copies of the recovery-related key records.In the event when there is a problem with the original copy, for recovery this portion is required.
NTFS File System Advantages
There are several advantages of the NTFS file system in comparison to predecessors like FAT. Some of these are:
- Filenames are saved in NTFS using UNICODE.
- On the NTFS configured volume, the files could be accessed easily and their names are also displayed correctly regardless of the system default encoding.
- An incorporated security system is there in NTFS having control of files sharing among the users.
- Privacy is guaranteed by various permissions levels, groups and owners.
- Files and folders could be encrypted or decrypted in NTFS while writing or reading them.
- Individual folders or files could be compressed or decompressed easily.
- The disk usage could be controlled by administrators with the help of user quotas introduced in NTFS. This helps in unfair behaviour prevention when all the disk space available is grabbed by a user for his demands while other users are left deprived.
- The NTFS file system can also complete the failed operation by restoring its state. The functionality of self-healing is there in NTFS 6.0 that is available with Windows Vista.
- NTFS has the ability to deal with large partitions and files successfully.
Overall, it could be said that the development of the NTFS file system is done keeping in mind all the lows and highs of other file systems such as FAT. New capabilities and technologies are taken into account by this, has the ability of privacy control and sharing an environment having multiple users.
Several handy features are also introduced by this such as NTFS symbolic links. This is a robust and stable file system and is therefore very much efficient and useful.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj