Tracking and restricting malicious network activities is one of the most critical and challenging tasks for network administrators. Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) are used by organizations to detect or block malicious traffic generated from the outside world. The situation became worse during the COVID pandemic where millions of workers were no longer working in traditional office setup but working from home, accessing data and network resources using unauthorized devices, unauthorized s/w and unsecured Wi-Fi.
Intrusion systems are crucial for small, medium, or large-scale businesses but licensed software is pretty expensive so if a lot of budget is not at the disposal, then open-source tools come handy such as Snort, Zeek, OSSEC, Suricata, security onion etc.
Today we will look more in detail Snort which is an open-source Intrusion application, its deployment, features, and comparison between Snort2 and Snort3 etc.
What is Cisco Snort?
Snort is the foremost Open-source Intrusion Prevention system (IPS) which was created in the year 1988 by Martin Roesch who is founder and former CTO of SourceFire. Later it was purchased by Cisco in 2013. Developed in C programming language to monitor the system in real time used as packet sniffer software.
The network administrators can use it to watch all incoming packets and find the ones which can be potentially dangerous for the network. It uses a library packet capture tool. It can be deployed on any kind of operating system such as Linux, Windows, Fedora, CentOS, FreeBSD and on any kind of network environment. Snort can operate on two modes – Sniffer mode and packet logging mode.
In Sniffer mode
To print TCP/IP header use ./snort – v command
To print IP address along with header use./snort -vd command
Packet Logging
To store packet on a disk, provide path where logs to be stored [./snort – dev -l./snortLogs] command
Activate network detection mode
Use command ./snort -dev – l./snortLogs -h 168.127.1.0/24 – c snort.conf
Features of Snort
- Real time traffic monitoring by packet sniffing by through examination of gathering individual packets which travel to and from devices in the network.
- Generates alerts or warnings on the basis of configuration file rules when it discovers any unusual or suspicious activity on the network.
- Debug traffic has been logged, any malicious packets and configuration issues are checked.
- Packet logging feature supported to store packets on a disk.
- Performs analysis of protocols.
- It performs content matching.
- It permits OS fingerprinting.
Snort Rules
Snort rules are distributed in two sets:
- Community ruleset and
- Snort subscriber ruleset.
Cisco Talos develops, tests, and approves the snort subscriber ruleset. Ruleset is received in real time by subscribers as released for Cisco customers. Community rulesets are freely provided to users by Snort community and QAed by Cisco Talos.
Snort supports three types of rules
- Alert rule – uses the alert technique for notifications
- Logging rule – each individual alert is logged as soon as it is generated
- Pass rule – Packet is ignored or dropped if it deemed suspicious or malicious
Cisco Snort 2
Architecture: Snort2 functions with multiple snort processes, each united to an individual CPU core and within each snort process there is a separate thread for management and handling of data.
Snort reload vs restart: Snort 2 requires restarting while policy deployment and attempting to reload snort instances.
Exception handling: Since each snort instance has its own process, only one snort instance is affected by forced exit and each crashed snort process will generate core dump.
Features:
- It is single threaded and slower.
- It supports policy binding at one level.
- Complexity is increased with shared memory usage.
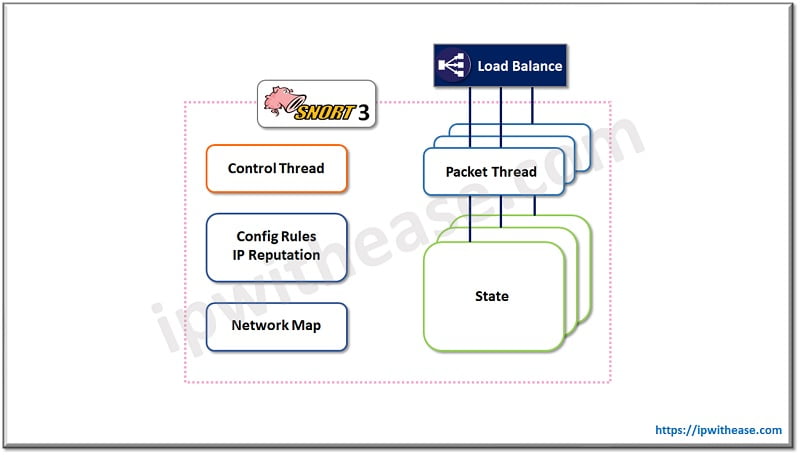
Cisco Snort 3
Architecture: Snort 3 only runs on one process, with each thread affiliated to an individual CPU core, with one backend control thread to handle.
Snort reload vs restart: Snort 3 shows improved traffic conservation during policy deployment and while attempting to reload snort instances.
Exception handling: Snort 3 instances run under the same process, so a fatal exception will cause the entire snort process to force exit and kill all snort instances.
Features:
- Reduction in memory and CPU usage.
- Improved HTTP inspection efficiency.
- Faster configuration load and restart for Snort.
- Faster feature additional enablement with better programmability.
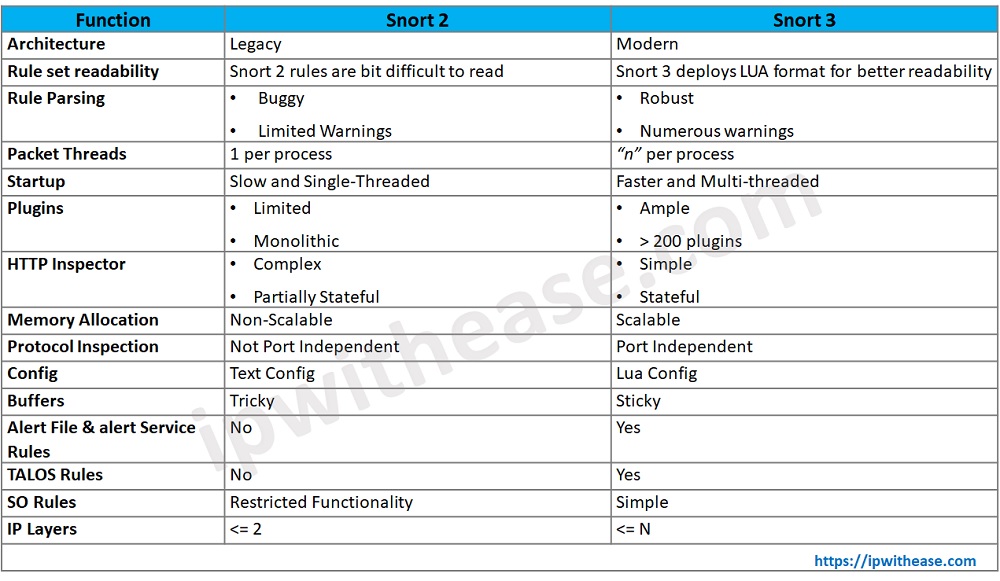
Cisco Snort 2 vs Snort 3
Below table summarizes the differences between the two versions of Snort:
Download the comparison table: Cisco Snort 2 vs Snort 3
Continue Reading:
IDS vs IPS vs Firewall – Know the Difference
What is IPS Security? Comprehensive Guide
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj