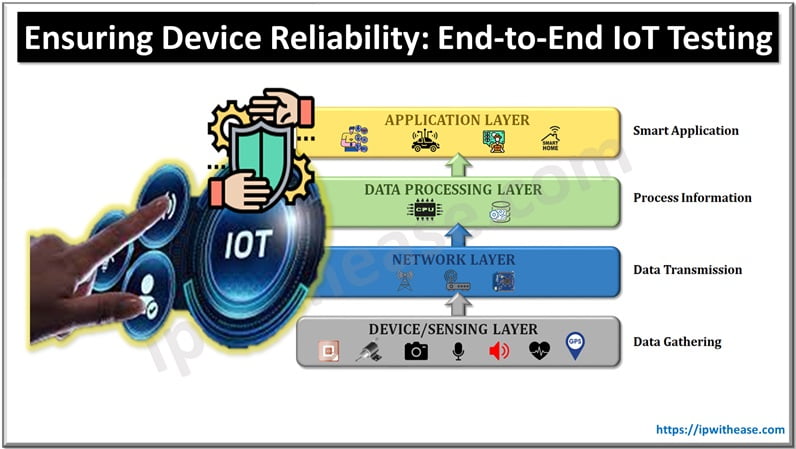
Table of Contents:
SSL Certificate is a digital certificate that enables an encrypted connection and authenticates a website’s identity. It is an acronym for Secure Sockets Layer, a setup that builds an encrypted link between your browser and the server.
Websites need to have SSL to secure online transactions and keep customer data safe and private. SSL secures internet connections and stops ill-meant entities from accessing and altering data transferred between two systems. The SSL symbol is the well-recognized padlock icon next to the URL.
There have been numerous SSL protocol versions since it was created about 25 years ago. All of these versions experienced security issues at one point. They were succeeded by a new version – Transport Layer Security (TLS), which is still being used – but the original acronym of SSL remained.
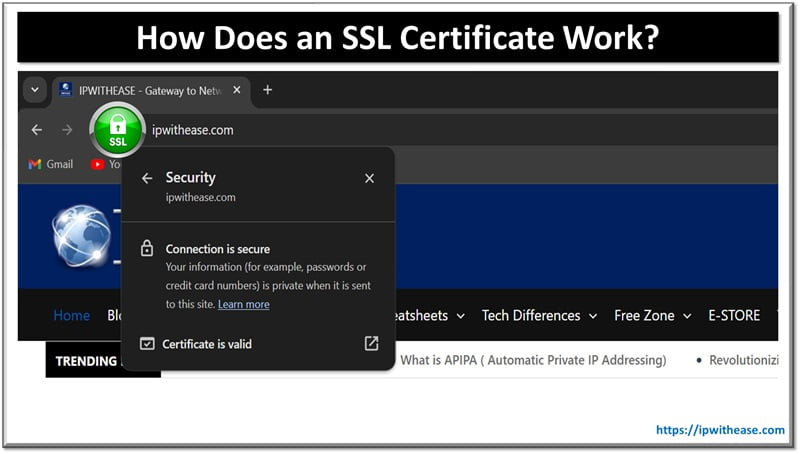
How Does SSL Work?
SSL works by making sure that all information transferred between two systems or between users and websites is impossible to read. It scrambles data as it’s being transferred using encryption algorithms, which stops hackers from reading it. This data includes personal and financial information such as:
- Names
- Email addresses
- Credit card numbers
- Login credentials
- Bank account information
- Dates of birth
- Telephone numbers
- Medical records
- Legal documents and contracts
- Proprietary information
This is how the process goes:
- A server or browser initiates a connection to an SSL-secured website
- It requests that the web server identify itself
- The site sends a copy of its SSL
- The server or browser confirms it’s valid
- An SSL-encrypted session starts.
The server or browser and the web server share encrypted data. The process is also known as an “SSL handshake” and transpires in milliseconds.
When an SSL certificate secures a website, the acronym HTTPS appears in the URL. Without an SSL, you will only see HTTP.
You click on the padlock symbol to view a certificate’s details. Typically, the following information is available:
- The person, device, or organization the certificate was issued to
- The domain name it was issued for
- The authority issuing it and its digital signature
- Any associated subdomains
- The certificate’s issue and expiration date
- The certificate’s public key
The risks of lacking SSL Certificate
A website needs SSL to verify its ownership, keep user data secure, stop cybercriminals from creating a fake version of the site, and communicate trust to visitors. Keeping data confidential is essential if a website is asking users to provide financial information, such as their credit card numbers, or view other private data, such as health benefits. SSL certificates assure visitors a site is safe to share private information with. They help keep online interactions private.
Final thoughts
You can’t have an HTTPS URL without SSL certificates, making them especially relevant for commercial entities. HTTPS sites have their traffic encrypted by SSL certificates. The majority of browsers label sites without SSL certificates as not secure. They also lower those sites’ search engine rankings. These elements are damaging to a website, mostly because they indicate to users the site can’t be trusted. A lack of an SSL can drive potential customers away if you’re operating a business.
Continue Reading:
SSL vs TLS: What is the difference?
What is Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS)?
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.