NAT Overload
NAT Overloading also called Port Address Translation (PAT) is a form of dynamic NAT where we have is just a single inside global IP address providing Internet access to all inside hosts. As a general case, cisco NAT Overload is used in scenarios where the number of inside local addresses is greater than the number of inside global addresses.
Related – NAT Types – Static, Dynamic And Overload
A simple scenario of cisco NAT Overload configuration will help the audience have a better understanding of Network address Translation concept and traffic flow across network elements.
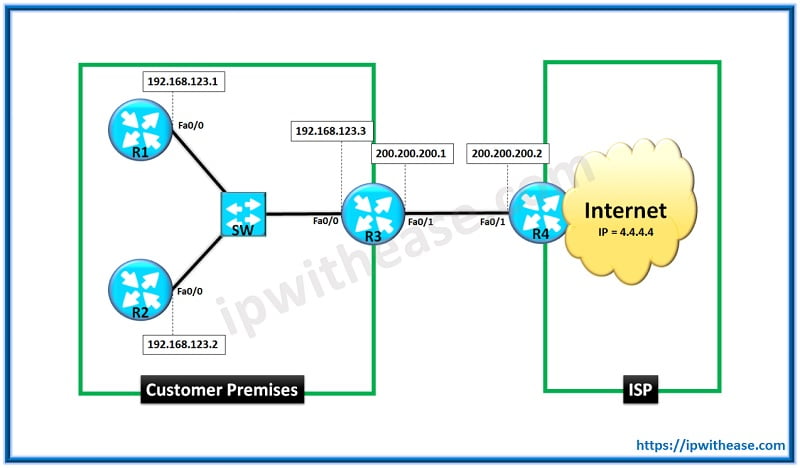
In the setup, R1 and R2 routers in LAN have been configured as end systems (host machines) which are connected through a Layer 2 Switch (SW) to customer Gateway Router (R3).
The Gateway Router is further connected to Internet Service provider (ISP). The customer has been assigned Public IP address by ISP as below –
- Set of Public IP 200.200.200.0/30 for WAN Connectivity to ISP
- Additional Public IP of 100.100.100.1 for customer access to the Internet.
In order for multiple LAN Users (192.168.123.0/24) to access the Internet via Single Public IP i.e. 100.100.100.1, NAT feature of “NAT Overload” will be used here. NAT Overload, also known as PAT (Port Address Translation) is essentially NAT with the added feature of TCP/UDP ports translation.
The configuration for each device is shown below –
R1 Configuration
R1(config-if)#ip addr 192.168.123.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no sh
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#no ip routing
R1(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.123.3
R2 Configuration
R2(config-if)#ip addr 192.168.123.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no sh
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#no ip routing
R1(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.123.3
R3 Basic configuration –
R3(config-if)#ip addr 192.168.123.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no sh
R3(config)#int fa0/1
R3(config-if)#ip addr 200.200.200.1 255.255.255.252
R3(config-if)#no sh
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 200.200.200.2
Now , we will configure R3 to perform NAT Overload as below –
R3(config)#ip access-list standard LANPOOL permit 192.168.123.0 0.0.0.255
R3(config)#ip nat inside source list LANPOOL pool NATPOOL overloadR3(config)#int fa0/0
R3(config-if)#ip nat inside
R3(config)#int fa0/1
R3(config-if)#ip nat outside
R3(config-if)#exit
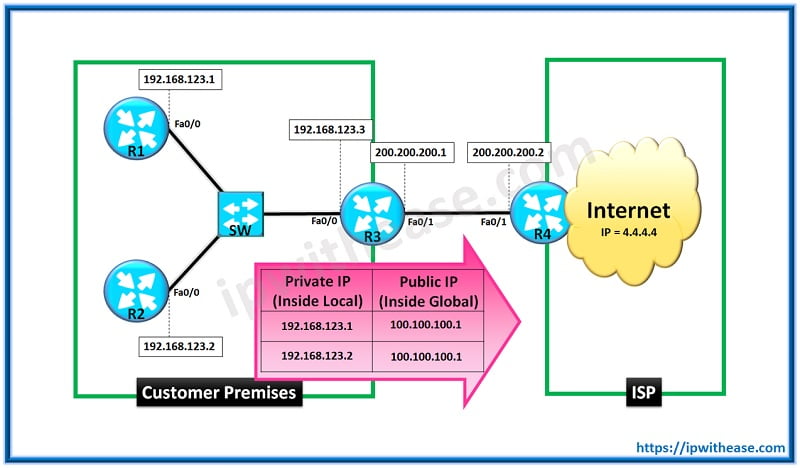
Once the NAT Overload configuration is complete, we will verify the same –
On R1 (ping any Global IP – In this case lets say 4.4.4.4) –
R1(config)#do ping 4.4.4.4
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 4.4.4.4, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 88/105/124 ms
Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global
icmp 100.100.100.1:5 192.168.123.1:5 4.4.4.4:5 4.4.4.4:5
Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global
icmp 100.100.100.1:5 192.168.123.1:5 4.4.4.4:5 4.4.4.4:5
icmp 100.100.100.1:0 192.168.123.2:5 4.4.4.4:5 4.4.4.4:0
Some more useful NAT commands are –
show ip nat statistics
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj


Thank you this is short and to the point! kudos!!