Digitalization has bought one hand major technological advancements however on the other end there is big and large volume of data generation happening from multiple sources. There are several analytical tools available in the market which could help in collecting, searching, monitoring, and analysing machine data to facilitate insight and intelligence into heaps of information which would be otherwise of no use or meaningful.
Today we look at one such analytical tool very popular in the field of data science and operational intelligence. We will learn how Splunk can help organizations to do application management, security, and compliance, Splunk architecture, its features and advantages.
Introduction to Splunk Architecture
It is a powerful platform for collecting, searching, monitoring, and analysing machine data. Heaps of unstructured data and logs coming in real-time from multiple devices can be pulled by Spunk in any format be it .csv, json, config files etc and structured to provide more meaningful insight.
Splunk is used by diverse clients in different industries all over the world ABN AMRO bank, Airbus, BOSCH, Coca-Cola, CSC, Dominos , Intel, Indiana university , Nasdaq, Nextra, Vodafone and many more. There are some good Splunk certification providers which include complete aspects of Splunk developer and Splunk administration.
History of Splunk
Splunk incorporation was founded in 2003 by Michael Baum, Rob Das and Erik Swan and by 2007 Splunk raised $40 million and started earning profits from 2009. In year 2012 Splunk was made public.
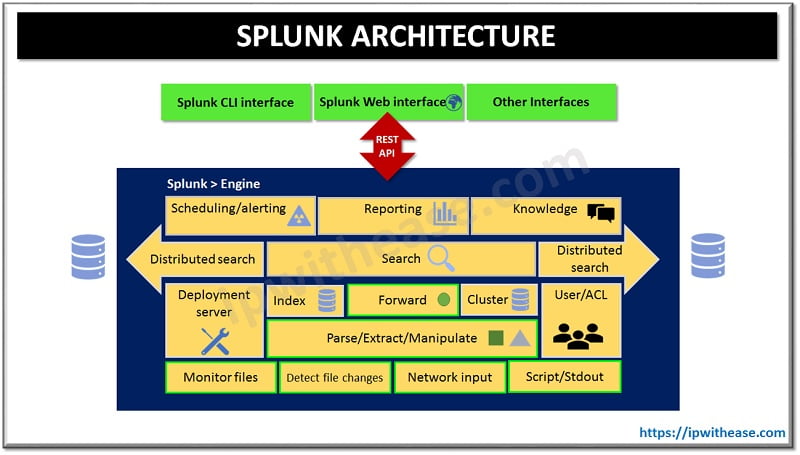
Splunk Architecture
The Splunk Architecture consists of three main Components:
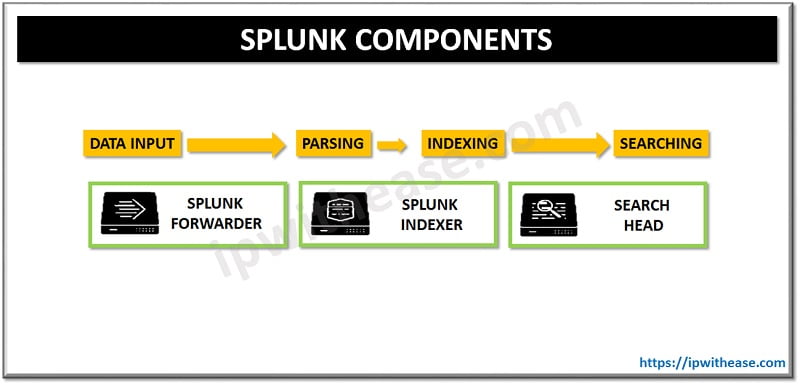
Splunk Forwarder – It is related to forwarding of data. This component collects logs and sends them to indexer. Multiple forwarders can be installed in array of machines and log data will be forwarded to Splunk indexer for storage and processing. Universal and heavy are two types of forwarder in Splunk.
- Universal Forwarder – not processed and treated but only raw data will be forwarded as it is.
- Heavy Forwarder – Parsing and indexing on host machine at the source.
Splunk Indexer – performs parsing and indexing. Indexer stores and indexes data which comes from forwarder. Indexer creates files in multiple formats and store them in buckets such as:
- compressed raw data
- indexes pointer toward raw data (.TSIDX files)
- Metadata files
Cluster of indexes can be setup with replication for redundancy on data loss.
Splunk Search Head – It is a GUI used to search, analyse and reporting purposes. Users can perform search and query Splunk data and interfaces with index to gain access for specific data request.
Splunk Features
Cloud and In-Premises powerful support – it is scalable, and services can be applied both to cloud and in premises. Users can access latest features on the cloud or manage the platform from public or private cloud environments.
AI and Machine learning is integrated – it is designed with integrated tools and supported by AI and ML algorithms. It can automatically identify, predict, and mitigate IT, security, DevOps and businesses errors.
Cloud Readiness – it can handle unexpected burst of data volumes and user can scale in the cloud as per the requirement.
Accessible through connected experiences – Platform is designed to offer access to a greater number of users such as mobile devices to establish communication with Splunk instances over encrypted bridge.
Quick answers via Analytics Workspace – It enables visualisation and alert on metrics or events data with drag and drop feature. Coverts logs into metrics to enhance monitoring experience.
Visualization and interactive dashboards – having services to create and distribute interactive dashboards and visualizations of data across the network.
Investigate approach – uses agile structure which help user to avoid data structure until specific query is made to software. Regardless of source or type ingestion of any data can be performed.
Scalable at enterprise level – Provides analysis with its powerful search capabilities which provide cohesion on analytical experiences with public data sets on any number of data sources.
Act on data in motion – It provides streaming processing service which provides a better control over exploration on organization data to have better view of environment and enhance business critical awareness for real time KPIs.
Pros and Cons of Splunk
Pros
- Easy to use
- Loads of Plugins and customization options
- Search and charting tools with attractive dashboards
- Fast data gathering
- Powerful analytical tool
Cons
- Expensive to deploy
- Must be scripted
- Licensing is per GB based and not on server
Continue Reading:
What is ISP (Internet Service Provider)?
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj