Table of Contents
Virtualization has drastically changed the way data centres were built earlier. The majority of modern data centres use hardware virtualization technology and deploy physical servers as hypervisors to run virtual machines on physical servers. This improves scalability, flexibility and saves operating costs.
Networks are the most crucial components of data centres along with virtualized data centres the need for large and complex network configurations for their virtualized environments. Software defined network architecture aims to make the network agile and flexible enough to respond to changing business requirements in a quick manner.
VMware NSX is a network virtualization solution which allows to build software defined networks in virtualized data centres. NSX comes in two different flavours: NSX-v and NSX-T
Today we look more in detail about two flavours of NSX namely NSX-v and NSX-T from VMware related to virtualization of network resources using NSX, their differences, advantages and so on.
What is NSX-v?
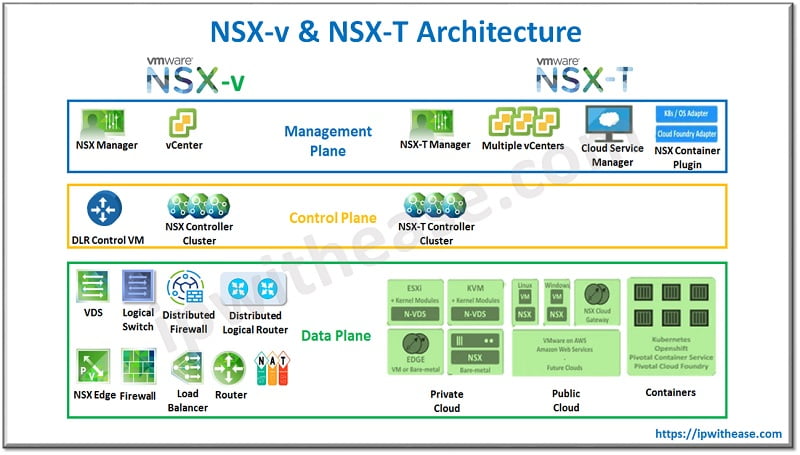
NSX-v was designed for vSphere deployments and architected on a single NSX-v manager platform tied to a single VMware vCentre server instance. NSX-v is the original NSX platform after VMware purchase in 2012 for Nicira.
It is tightly integrated with VMware vSphere and specific to vSphere hypervisor environments developed before NSX-t. Deployment of NSX-v and t are quite similar. NSX manager is deployed as VM on an ESXi host using a virtual appliance but ensure to register NSX manager on vSphere vCentre for NSX-v.
Install VIBs (kernel modules) on ESXi hosts to enable a distributed firewall, routing and VXLAN if using NSX-v. Install NSX edge as VM on ESXI (for NSX-v). NSX for vSphere uses DLR or distributed logical router and centralized routing. Routing kernel module is present on each hypervisor to perform logical routing between interfaces on distributed routers.
Features of NSX-v
- NSX-v offers integration with 3rd party services such as agentless antivirus, firewalling, intrusion detection and prevention systems, traffic inspection services
- Kernel level distributed firewalls
Use case for NSX-v
- Secure end user
- DMZ anywhere
- Application continuity
- Disaster recovery
- Multi data center pooling
- Cross cloud
What is NSX-T?
VMware NSX-T is the next generation modern VMware NSX data center solution. It covers all VMware platforms including vSphere. The ‘T’ stands for ‘Transformers. It lets you transform the initial use case of network virtualization with NSX-v into the kingdom of public cloud and modern workloads containerization.
It is designed for different virtualization platforms and multi-hypervisor environments and can also be used where NSX-v is not feasible to deploy. NSX-T supports network virtualization stack for KVM, Docker, Kubernetes and OpenStack as well as AWS native workloads. It can be deployed without a vCenter server and used across heterogeneous computing systems.
NSX manager can be deployed as a virtual appliance on a KVM host as VMware NSX-T to create a cluster of NSX managers. Kernel modules should be installed on KVM hypervisors. There is no possibility of installation of edges as virtual machines on ESXi in case of NSX-T. Edge installation over the KVM hypervisor is not supported.
Features of NSX-T
- Scale out networking by federating and management of numerous installations of VMware NSX across multiple locations
- Offers full stack networking for modern applications
- Intuitive dashboard and capabilities
Use cases for NSX-T
- Micro segmentation
- Automation of IT
- Developer cloud
- Multi-tenant infrastructure
Comparison Table: NSX-T vs NSX-v
Below table summarizes the difference between the two:
Function | NSX-T | NSX-v |
| Pre-requisites (vCenter server dependency) | Does not require vCenter server and let you directly interact with ESXi hosts and onboard them as transparent nodes | It is VMware vSphere solution only. Requires connection to vCenter server for integration with ESXi hosts |
| Overlay Technology | Uses generic network virtualization encapsulation (GENEVE) as the overlay network encapsulation protocol | Uses virtual extensible LAN (VXLAN) as overlay technology which creates virtualized network infrastructure |
| MTU | Minimum 1700 bytes | Minimum 1600 bytes |
| Routing | Uses multi-tier routing architecture known as TIER-0 and TIER-1 routing topology | Uses traditional routing structure |
| Multi cloud capabilities | True multi cloud platform which allows virtual networking capabilities leveraging in both on premises and cloud | Limited to vSphere environments hence not considered a multi cloud platform |
| Life cycle | NSX-T is successor to NSX-v | Going to be end of life in year 2022 and extended technical guidance will end in year 2023 |
| Features | It can work without vCenter, it supports two tier distributed routing, it supports kernel level distribution firewall etc. | It supports ARP suppression, IP address scheme configuration is performed manually, it cannot work with vCenter etc. |
| Hypervisor Support | VMware ESXi, KVM, Kubernetes, Docker, Public cloud workloads(AWS, Azure, Google), etc. | VMware ESXi |
| NSX Manager & Controller | NSX management can have upto 3 member clusters, with independent NSX managers to avoid an outage. | NSX controller deployed as 3-node cluster to a single NSX manager (& hence a single point of failure) |
| Overlay Switching | Uses N-VDS for ESXi and OVS (Open vSwitches) for KVM hosts | Creates logical networks on top of VDS (vSphere Distributed Switch) |
| Kubernetes Support | Using NCP (NSX Container Plug-in) | No Support |
| Supported Environments | Supports multi-cloud, multi-hypervisor & bare metal workloads. It also supports cloud native apps | Best Suited for On-premise workloads |
Download the comparison table: NSX-T vs NSX-v
Continue Reading:
ESX vs NSX: Detailed Comparison
Cisco ACI benefit over VMware NSX
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj



