Cisco Hierarchical Model
Cisco Hierarchical Model
Cisco three Layer Hierarchical Model aims at building a reliable, scalable, and high-performance Network Design. This high-performance network Hierarchical approach provides a cost-effective, modular, structured & Simple approach ( furnishes an uncomplicated and uniform design) to address existing and future growth requirements. Each layer has its own features and functionality, which further reduces the network complexity.
Requirements for Cisco Hierarchical Model
The functional requirements which lead to setting up a Cisco three layer hierarchical model approach are as shared below –
- Scalability – Efficiently accommodates future growth.
- Ease of Management and troubleshooting – Efficient management and simple in isolation of failure cause.
- Simpler and Structured filtering and Policy enforcement – Simpler to create filter/policy and enforce on network.
- Redundancy and Resiliency – Network should tolerate faults/downtime of device and keep providing services with same performance when the primary device fails.
- High performance – Hierarchical architecture to support high throughput and high performance underlying Active Infrastructure.
- Modularity – Allows flexibility in network design and facilitates simple implementation and troubleshooting.
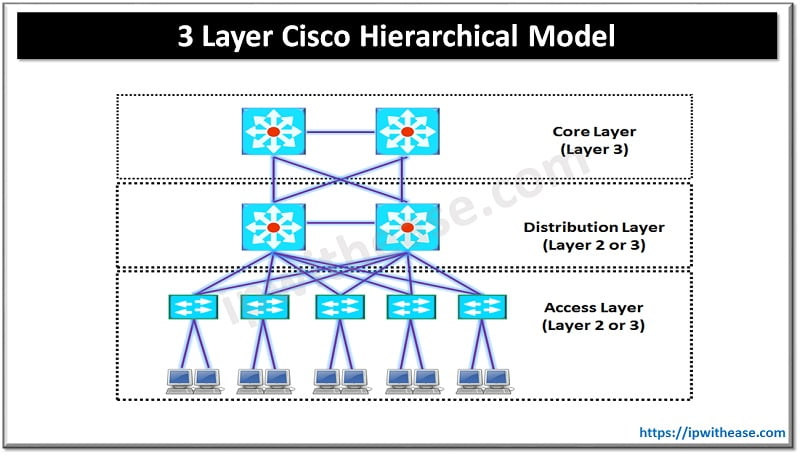
3 Layer of Cisco Hierarchical Model
Core Layer –
This layer is also referred to as Network Backbone Layer and is responsible for providing fast transport between distribution switches within the enterprise campus.
Core layer stations high end and high throughput switches having modular form factor. These are fully redundant devices supporting advanced Layer 3 switching features and dynamic routing protocols. A key consideration is to keep the configuration as minimal as possible at Core Layer.
Due to the very high criticality of this layer, design, this layer requires a high level of resilience in order to recover quickly and smoothly after any network failure event within Core block.
Below are the key features of the Core Layer –
- High performance and through switching
- Providing reliability and fault tolerance
- Scalable
- Avoiding CPU-intensive packet manipulation caused by security, inspection, quality of service (QoS) classification, or other processes
Some models of Cisco Switches running on Core Layer are Catalyst 9500/6800/6500 Series and nexus 7000 Series.
Distribution Layer –
Distribution Layer is located between the access and core layers. This Layer’s primary function is to provide routing, filtering, and WAN access and to render communication between Access and Core layer.
Additionally, distribution layer switches may provide upstream services for many access layer switches. Distribution Layer ensures that packets are routed between subnets and Inter/Intra VLANs within the Campus environment.
As a standard approach, Default Gateways for all the VLANs will be the Distribution layer Switches.
In fact, the server devices should not be directly connected to the distribution switches. This approach provides the benefit of saving cost per port due to high port density at less costly Access Layer Switches.
Primary functions of Distribution Layer are enlisted below –
- Accumulation of LAN / WAN links.
- Access Control and Filterings like ACLs and PBR.
- Routing between LANs and VLANs and between routing domains
- Redundancy and load balancing.
- Subnet Summarization and route aggregation at boundaries/towards Core Layer.
- Broadcast domain control. The distribution layer device acts as the demarcation point between broadcast domains.
Primary models of Cisco Switches running on Distribution Layer are Catalyst 6800/6500/4500/3850 Series.
Access Layer –
This layer includes Layer 2 switches and access points that provide connectivity to workstations and servers. On the uplinks, the Access Layer devices are connected to Distribution Switches.
We can manage access control and policy, create separate collision domains, and provision port security at the Access layer.
Access layer switches ensure that packets are delivered to the end devices.
The access layer serves a number of functions, including –
- Layer 2 switching
- High availability
- Port security
- QoS classification and marking
- Trust boundaries
- Access control lists (ACLs)
- Spanning tree
Primary models of Cisco Switches running on Access Layer are Catalyst 3850/3750/4500/3560/2960 Series.
Continue Reading:
Hope you would have understood the cisco hierarchical model through this article. Please read our other articles for more information –
VPN Top 100 Interview Questions
Introduction to Distributed vSwitch
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj

 Cisco Hierarchical Model
Cisco Hierarchical Model