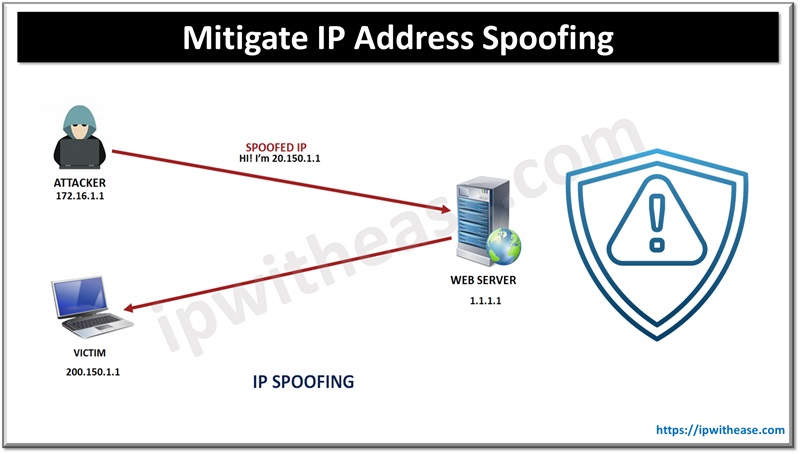
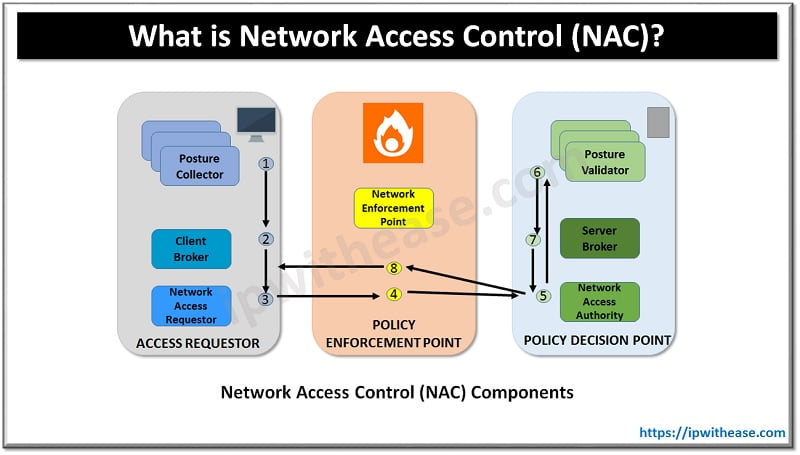
Table of Contents
Effective and efficient management of security incidents is extremely critical in IT operations as service disruptions are costly affairs. Businesses dependencies on infrastructure, cloud computing are increasing so as the risks of cyber attacks and threats.
Incident response and incident management both terms are used interchangeably however, they are meant to address different purposes and maintain customer trust and reliability of systems.
A typical response to a disruptive event or occurrence usually adopted by organizations to contain the damage. It is a reactive action to a specific situation and try to resolve it as soon as possible as this is considered as the first line of defence and objective is to restore systems to their previous stable state.
Incident management is a strategic approach towards an event or disruption. This process covers complete lifecycle management of an incident starting from its groundwork, response, resolution and learnings.
In today’s article we will understand the difference between incident response and incident management, its key characterises and stages.
What is Incident Response
A typical response to a disruptive event or occurrence usually adopted by organizations to contain the damage. It is a tactical response to an unforeseen event and aim is to restore services to its original state before disruption had occurred and minimize the cost of cyberattack. A carefully crafted incident response can fix a potential breach or vulnerability and prevent any future cyberattacks. Data breaches cost businesses time, reputation, financial losses and depleted brand image. Organizations need a well-structured incident response plan which aims at
- Restoring business operations to normal state
- Contain financial and reputational losses
- Fixing vulnerabilities in timely manner to reduce threat landscape
- Avoiding future attacks by strengthening the security posture
Stages of Incident Response
A typical incident response plan has the following stages.
Step 1: Detection of incident via monitoring , alerts or user reports
Step 2: Diagnosis and assessment is done which is preliminary investigation to understand incident scope and impacted resources and services
Step 3: Escalation process engages right stakeholders and internal teams to work on fixing the issue
Step 4: Communication involves keeping all relevant teams and stakeholders and customers informed
Step 5: Containment limits the damage it involves isolation of impacted systems and services
Step 6: Resolution involves fixing the issue and restoring systems to normalcy
What is Incident Management
Incident management is a broader concept and a strategic approach towards overall management of the incident lifecycle starting from its occurrence, preparation, response, mitigation and learning. It is a means to provide a standard and consistent approach towards handling overall incidents and minimize business disruptions.
Salient features of incident management are:
- Planning, coordination and process improvement is the focus here
- Have measures to address both reactive and preventive incidents and their effective handling
- Focus is long term as the aim is to reduce likelihood of incidents and build overall resiliency.
Stages of Incident Management
A typical incident management has the following stages.
Step 1: Preparation – develop policies, procedures and tools to handle security incidents efficiently
Step 2: detection of incidents via monitoring tools , user actions and alerts
Step 3: diagnosis and assessment to understand issue scope and impact
Step 4: escalation process involves engaging right stakeholders to address the incident
Step 5: communication involves keeping all relevant stakeholders and customers informed about the incident
Step 6: Containment involves damage control practises
Step 7: Resolution involves mitigation of incident and restoring operations back to normalcy
Step 8: learning and documentation involves analysis of incidents, its root cause analysis and implement detective and preventive controls
Comparison: Incident Response vs Incident Management
| Features | Incident Response | Incident Management |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Tactical in nature, reactive to a situation focus is to handle immediate situation | Strategic in nature, preventive to a situation and aim is to plan and strategize how to reduce / prevent future incidents |
| Objective | Quicker mitigation of issue and bring systems back to normalcy as soon as possible | Entire lifecycle management of incidents starting from its detection, preparation, diagnosis, assessments, mitigation and learnings. |
| Responsibility | Incident response primarily responsibility lies with organization security teams, security engineers and threat hunters. | Since it is strategic in nature in involves multiple stakeholders from different teams – management and IT teams |
| Timeframe | Focus here is to fix the issue in hand and restore operations to normalcy | Focus is on long term resolution of future issues and continuous improvement |
| Scope | Scope is limited to incident occurred | Scope is vast it involves overall all management of incidents holistically |
| Impact | Incident response is activated as soon as incident is hit as it impacts the availability of systems, services and data | Incident management is long term perspective on handling incidents and it impacts service availability and quality over a period of time |
Download the comparison table: incident response vs incident management
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj