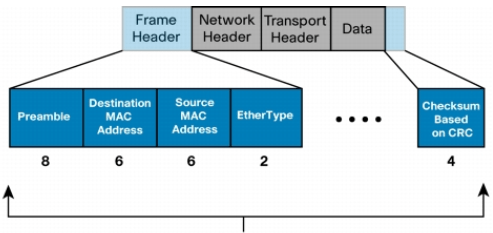
LAN SWITCH MODES
LAN switching uses hardware destination as the basis to forward and filter frames. LAN switch types determine the way in which a frame gets processed when the frame arrives at a switch port. Infact, switch modes type plays an important role when end-to-end application latency requirements is the key customer ask. This latency does vary and depends on what type of switching mode the switch is operating at. To recall, there are three switching modes of LAN Switching –
- Store & Forward
- Cut-Through and
- Fragment Free.
The earliest method of forwarding data packets at Layer 2 was referred to as “store-and-forward switching”. In most data center and other networking environments, both cut-through and store-and-forward LAN switching technologies are suitable.
STORE AND FORWARD MODE –
Note – In above shown figure , Store and Forward Switching waits for receipt of entire frame upto 9200 Bytes before forwarding decision is made.
In Store-and-forward mode, switch waits for whole of frame to be received and at the end of that frame, the switch will compare the last field of the datagram against its own frame-check-sequence (FCS) calculations, to help ensure that the packet is free of physical and data-link errors. The switch modes then performs the forwarding process.
If a Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) error is found, the Ethernet frame is dropped and if there is no Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) error, the switch then performs the forwarding process to the destination device.
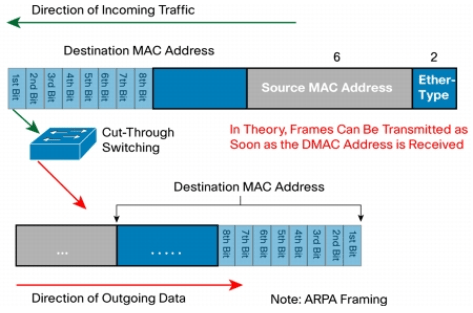
CUT-THROUGH MODE –
As shown in the above figure , when a frame is received, the switch copies the destination address to its onboard buffers. The fact that the frame is forwarded as soon as the destination address is read and the outgoing interface is determined, results in decreasing latency. However, we have caveat here – With cut-through switching the Switch may forward bad frames.
FRAGMENT FREE MODE –
In Fragment Free mode, the switch first checks the initial 64 bytes of a frame for fragmentation before the frame is forwarded. This is done to avoid possible collisions. While cut-Through mode only considers the destination mac address before forwarding the frame , Fragment free checks the atleast 1st 64 bytes before forwarding the frame towards destination.
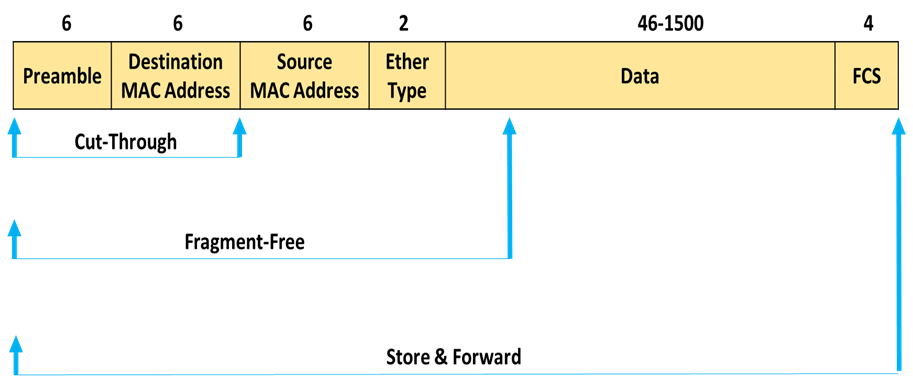
Below Picture clearly depicts the 3 types of Switching modes –
- Cut-Through forwards frame only after reading the Destination Mac address.
- Fragment Free checks atleast 64 Bytes of data before forwarding the frame.
- Store and forward only forwards the frame after whole frame is read , CRC carried and then it takes decision to forward if no errors found.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj