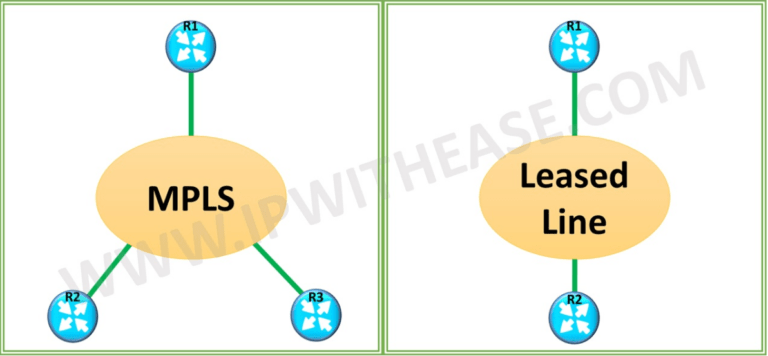
MPLS –
“MPLS” is an abbreviation for “Multiprotocol Label Switching.” Data packets are assigned labels in an MPLS network. Instead of examining the packet, packet-forwarding decisions are made based purely on labels.
MPLS guides data from one node to the next based on labels for path instead of network addresses, avoiding complex lookups. At every point, a new label is attached to the packet until it reaches the destination.
MPLS guides data from one node to the next based on shortest labels for path instead of network addresses, avoiding complex lookups.
Related – MPLS vs VPN, MPLS vs VPLS, MPLS Cheatsheet
Leased Line –
A leased line is dedicated and high-speed connectivity built across two sites. Leased lines do not share the connectivity with any other customer and we get symmetric speed in both directions.
It is sometimes also known as a ‘Private Circuit’.Leased lines are older technology than MPLS and have been around a bit longer.
Related – Leased Line vs Broadband
Both Leased Lines and MPLS are available over copper and Fiber medium and support high bandwidths up to Gbps. Additionally both support voice and data services, however, there are parameters on which they differ.
MPLS vs Leased Line –
| PARAMETER | MPLS | LEASED LINE |
|---|---|---|
| Segregation of customer traffic | Logical separation of customer traffic. | Physical separation of customer traffic |
| Connectivity Type | Multipoint or point-to-Point | Point-to-Point |
| Security | High level by logical separation of traffic | Most secured due to physical separation of traffic |
| Skill Requirement | Highly skilled resources at Provider/customer end for deployment of MPLS. | Less skilled resources required for setup of Leased links. |
| Bandwidth | High | High |
| Spoke to Spoke communication | Remote site needs to traverse viz Hub site to reach other remote site | Direct any to any communication from one Spoke to other |
| CAPEX and OPEX | Usually lower cost than P2P Leased links | Higher than MPLS Links |
| Physical medium | Shared across multiple customers | Dedicated to customer |
| Performance | Improved performance especially when Spoke to Spoke communication | Low performance in Spoke to Spoke communication since HUB incurs additional hop which is not the case in MPLS |
| Routing decision | Service provider is involved in Layer 3 Routing of the customer traffic | Service provider does not involve in Routing decision of customer traffic. |
| QOS | Service provider QOS for prioritization of delay sensitive and mission critical traffic. | Partially or no QoS |
| Traffic Engineering | In MPLS it is possible to set the path that the traffic will have to take through the network. | Not possible in case of Leased links. |
| Scalability | MPLS is as an efficient technology that is easily scaled. | Leased lines are the most difficult to scale, both because of the time needed for deployment and the expense. |
| Recommended for | * Large enterprise with a requirement for secure and private network * Have multiple sites spread across a large area. * Fast growing organization with inorganic growth of sites | * Require guaranteed bandwidth * Need to transfer large data reliably and fast between sites |
![]()
Download the difference table here.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj