MPLS vs VPN technology
MPLS vs VPN technology
VPN and MPLS are widely used technologies for connecting across HUB and remote sites. IPSec VPN being the 1st entrant of 2, was quite a hit since it leveraged the Internet connectivity while providing security and access to central Data Center applications.
The need for improved customer experience and reliability led to invent of MPLS which further benefited by allowing overlapping customer IP subnets to communicate across the same Provider infrastructure
In MPLS vs VPN comparison, the drawback is with VPN technology being overhead (bits used in encryption) and latency which is not substantial in case of MPLS.
In fact, multicast and Dynamic Routing protocol traffic traversal via IPSec tunnels requires the additional overhead of GRE tunnel creation (additional bits used for GRE header).
VPN generally works on the Internet which is cheaper than MPLS( read this WAN connectivity pricing guide for further details) however, using the Internet is less stable and traffic flows on best effort basis. In fact, using delay-sensitive and mission-critical media over VPN will not be a wise decision.
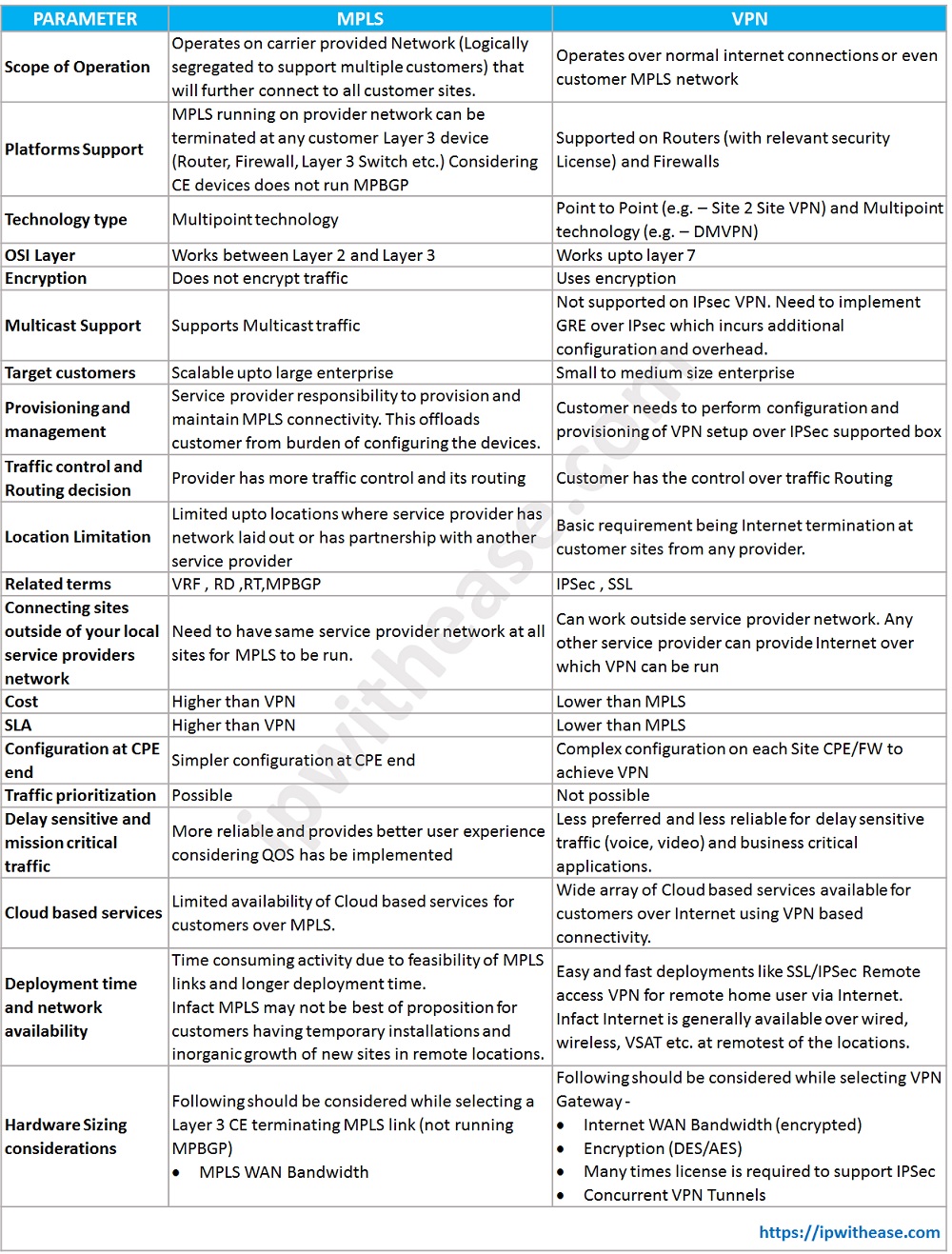
Comparison Table : MPLS vs VPN Technology
| PARAMETER | MPLS | VPN |
|---|---|---|
| Scope of Operation | Operates on carrier provided Network (Logically segregated to support multiple customers) that will further connect to all customer sites. | Operates over normal internet connections or even customer MPLS network |
| Platforms Support | MPLS running on provider network can be terminated at any customer Layer 3 device (Router, Firewall, Layer 3 Switch etc.) Considering CE devices does not run MPBGP | Supported on Routers (with relevant security License) and Firewalls |
| Technology type | Multipoint technology | Point to Point (e.g. – Site 2 Site VPN) and Multipoint technology (e.g. – DMVPN) |
| OSI Layer | Works between Layer 2 and Layer 3 | Works upto layer 7 |
| Encryption | Does not encrypt traffic | Uses encryption |
| Multicast Support | Supports Multicast traffic | Not supported on IPsec VPN. Need to implement GRE over IPsec which incurs additional configuration and overhead. |
| Target customers | Scalable upto large enterprise | Small to medium size enterprise |
| Provisioning and management | Service provider responsibility to provision and maintain MPLS connectivity. This offloads customer from burden of configuring the devices. | Customer needs to perform configuration and provisioning of VPN setup over IPSec supported box. |
| Traffic control and Routing decision | Provider has more traffic control and its routing | Customer has the control over Traffic Routing |
| Location Limitation | Limited upto locations where service provider has network laid out or has partnership with another service provider | Basic requirement being Internet termination at customer sites from any provider. |
| Related terms | VRF, RD, RT, MPBGP | IPSec , SSL |
| Connecting sites outside of your local service providers network | Need to have same service provider network at all sites for MPLS to be run. | Can work outside service provider network. Any other service provider can provide Internet over which VPN can be run |
| Cost | Higher than VPN | Lower than MPLS |
| SLA | Higher than VPN | Lower than MPLS |
| Configuration at CPE end | Simpler configuration at CPE end | Complex configuration on each Site CPE/FW to achieve VPN |
| Traffic prioritization | Possible | Not Possible |
| Delay sensitive and mission critical traffic | More reliable and provides better user experience considering QOS has be implemented | Less preferred and less reliable for delay sensitive traffic (voice, video) and business critical applications. |
| Cloud based services | Limited availability of Cloud based services for customers over MPLS. | Wide array of Cloud based services available for customers over Internet using VPN based connectivity. |
| Deployment time and network availability | Time consuming activity due to feasibility of MPLS links and longer deployment time. Infact MPLS may not be best of proposition for customers having temporary installations and inorganic growth of new sites in remote locations. | Easy and fast deployments like SSL/IPSec Remote access VPN for remote home user via Internet. Infact Internet is generally available over wired, wireless, VSAT etc. at remotest of the locations. |
| Hardware Sizing considerations | Following should be considered while selecting a Layer 3 CE terminating MPLS link (not running MPBGP) * MPLS WAN Bandwidth | Following should be considered while selecting VPN Gateway - * Internet WAN Bandwidth (encrypted) * Encryption (DES/AES) * Many times license is required to support IPSec * Concurrent VPN Tunnels |
![]()
Download the difference table here.
Continue Reading:
MPLS vs IP Routing : Know the difference
Watch our related video for more understanding:
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj

 MPLS vs VPN technology
MPLS vs VPN technology