Table of Contents
What is SAML?
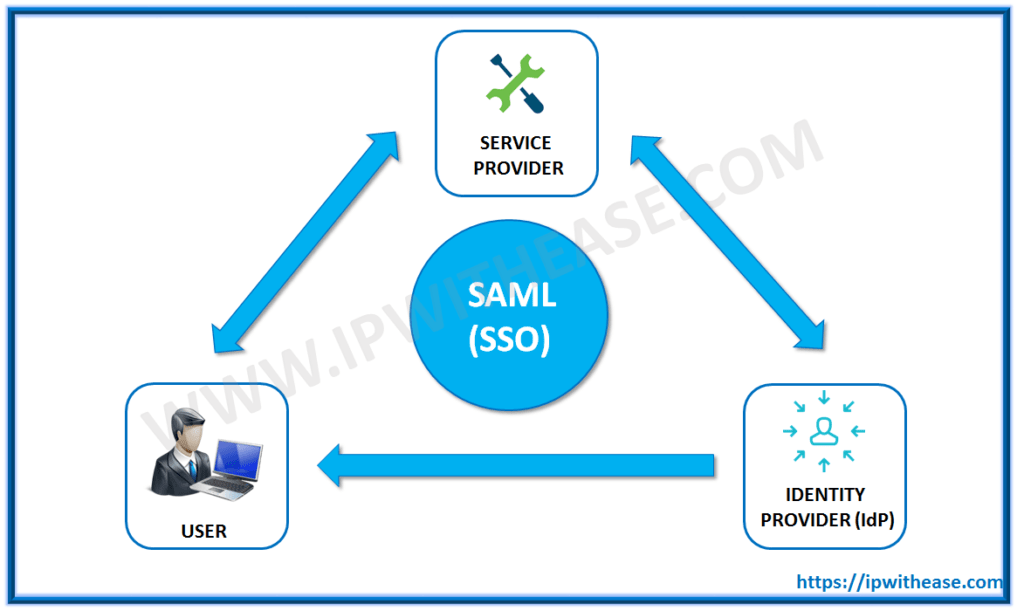
SAML is an abbreviation for Security Assertion Markup Language. SAML’s key benefit is that it allows single sign-on capabilities for Web Services/applications. Another SAML definition is an open standard that enables web browser single sign-on through the exchange of an assertion between an Identity Provider and a Service Provider.
It describes a framework that allows one computer to perform some security functions on behalf of one or more other computers like authentication and authorization.
SAML Terminologies –
- Assertion – XML passed between the Service provider and identity provider.
- Assertion Consumer Services (ACS) – Target resource within the SP where the IDP sends the SAML response assertion to.
- Attribute – Unique information about a user that is passed within an assertion.
- Identity Provider (IdP) – A trusted entity providing authentication services to the SP on behalf of the user principal.
- Issuer – A unique string that must match in both the IdP and SP.
- SAML Request – An assertion that the SP passes to the IdP to request a user to be authentication.
- SAML Response – An assertion that the IDP passes to the SP for an authenticated user.
- Service Provider – The web application that the user wants to access.
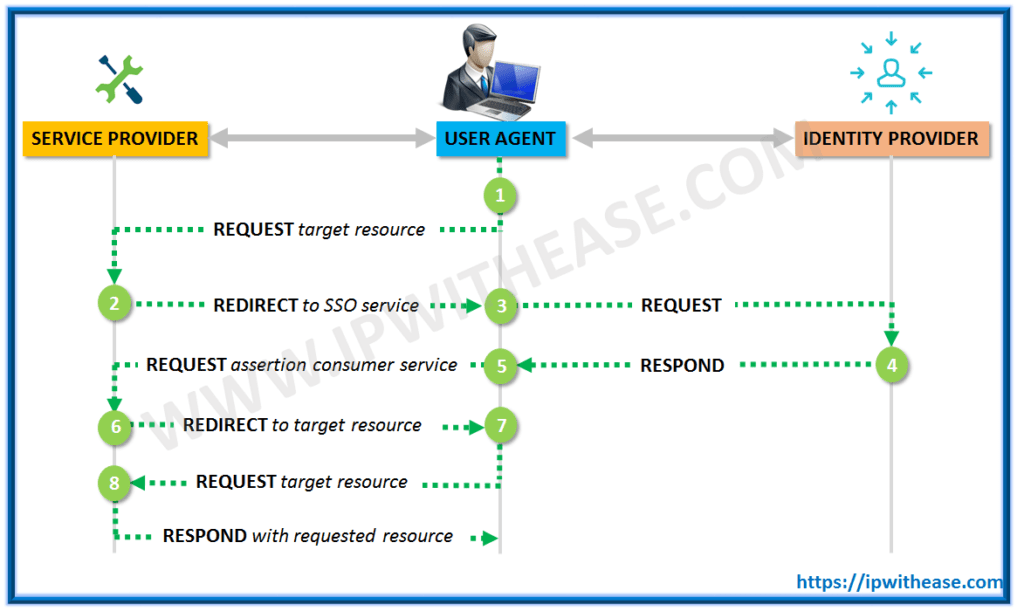
SAML Authentication –
Step by Step SAML Authentication Process –
Step 1 – In the first step of SAML Authentication, the user tries to access the application/web service (Service provider). The service provider verifies if the user already authenticated within the system.
If the user is already authenticated, content can be made available directly to the user. Else, if the user is not authenticated, the service provider starts the authentication process.
Step 2 – The service provider determines the identity provider and a redirects user request to that provider ie single sign-on service.
Step 3 – In the third step of SAML authentication, user browser sends an authentication request to the SSO service.
Step 4 – The SSO service returns a request which includes the authentication information needed by the service provider in a SAMLResponse parameter.
Step 5 – The SAMLResponse parameter is passed on to the service provider.
Step 6 – The service provider processes this response and allows the user to log in and informs where the user-requested resource is.
Step 7 – User can now request the resource he wants.
Step 8 – The resource is finally returned.
Hope you would have understood What is SAML & SMAL Authentication. Read our other similar articles –
Upgrades to SAML (security assertion markup language) versions over time –
- SAML 1.0 was adopted in November 2002
- SAML 1.1 was ratified in September 2003
- SAML 2.0 became an OASIS Standard in March 2005
SAML FAQs
Q.1 What is Authentication?
Authentication is the process of validating the identity of the client. This is to make sure that the user connecting to a system is authorized and allowed for the login. SAML is one of the language to get this.
Q.2 What is SAML?
SAML is a Security Assertion Markup Language. SAML’s key benefit is that it allows single sign-on capabilities for Web Services/applications. Another SAML definition is an open standard that enables web browser single sign-on through the exchange of an assertion between an Identity Provider and a Service Provider. SAML is a framework that allows security functions like authentication and authorization.
SAML Processes
There are two types of SAML processes:
IDP-initiated SSO — The client connects to the identity provider, gets authenticated, and then accesses the resources from the service provider.
SP-Initiated SSO — The client connects to a service provider, which then redirects the client to the identity provider for authentication. Once successfully authenticated, the client is then redirected to the service provider. Which allows access to the resource.
SAML Bindings
The IDP and SP exchange a SAML request/response with each other through the client. Exchanging these messages is called a SAML binding. SAML supports many kinds of bindings.
POST binding, client send this response to the SP. The SAML response is transmitted in an HTML form.
Redirect the binding, client to the IDP. The SAML request is carried in the URL query string of an HTTP GET request.
Q.3 How Does SAML Work?
SAML passes information about user’s login and attributes between the identity provider and service provider. When user logs into Single Sign On with the identity provider, then identity provider passes SAML attributes to the service provider for the user to attempt and access those services. SP requests the authorization and authentication from the IDP. Identity provider and Service provider need to agree upon the configuration for SAML and both ends must have the exact configuration for the SAML authentication to work.
SAML authentication process:
– The end user initiates a session with an identity or SSO provider by logging in and being authenticated.
– The end user initiates a session with a service provider cloud application or other third-party application which is configured to do authentication via SSO.
– The service provider requests authentication information about that specific user from the end user’s identity provider.
– The identity provider responds to the SAML request with a SAML formatted, digitally signed response that identifies the end user and may include further information indicating that the user is or is not authenticated and authorized or not to access restricted resources.
– The service provider validates the response from the identity provider and authenticates the end user to give them access to restricted resources.
– The end user accesses the service provider’s content or application.
Requests and responses to those requests must conform to the SAML protocols for exchanging information with SAML data being formatted as assertions.
Q.4 What is SAML ASSERTION?
SAML assertion is the XML document that IDP sends to the SP and contains the user information attributes. There are three different kinds of attributes in SAML assertions: authentication, attribute and authorization.
Authentication Assertion — Authentication assertion proves identification of the user and provides the time stamp logs when the user logged in and what method of authentication they used I.e. Kerberos.
Attribute Assertion — Attribute assertion passes the SAML attributes to the SP. SAML attributes provides information about the user.
Authorization Assertion — Authorization decision assertion states if the user is authorized to use the service or if the IDP denied their request due to a password. User may not be allowed to use the service.
Q.5 Explain SAML Request/Response
SAML Responses
SAML Response is sent by the IDP to the SP. If user succeeds in the authentication process, it contains the assertion with the NameID attributes of the user. There are 8 examples:
1. Unsigned SAML Response with an unsigned Assertion.
2. Unsigned SAML Response with a signed Assertion.
3. Signed SAML Response with an unsigned Assertion.
4. Signed SAML Response with a signed Assertion.
5. Unsigned SAML Response with an encrypted Assertion.
6. Unsigned SAML Response with an encrypted signed Assertion.
7. Signed SAML Response with an encrypted Assertion.
8. Signed SAML Response with an encrypted signed Assertion.
SAML AuthNRequest
An AuthnRequest is sent by the SP to the IDP in the SP-SSO initiated flow.
Below are 2 examples:
1. An AuthnRequest with its Signature (HTTP-Redirect binding).
2. An AuthNRequest with the signature (HTTP-POST binding).
Q.6 Describe the concept of SAML Single Sign-On.
SAML is an XML based open-standard data format for exchanging authentication and authorization attributes between an Identity Provider (IdP) and a Service Provider (SP). The requirement of SAML addresses is web browser single sign-on (SSO). SAML 2.0 is the industry standard for identity management based on Single Sign-On (SSO). SSO is a user authentication process that permits a user to enter the same name and password to access multiple web applications.
Q.7 What are the benefits of using SAML SSO?
1. Provides security controls through security policies across all applications.
2. Reduces turnaround time for provisioning and de-provisioning of user accounts in applications.
3. Faster identity data collection access reviews and security analytics.
4. Provides single sign on experience for end users.
5. Enables new users to gain faster access to the resources.
6. Eliminates or reduces duplicate user ID.
Q.8 What are SAML Tokens?
SAML tokens are set of claims made by one entity about another entity. Security token service signs the SAML token. The SAML token contains cryptographic key. This is the proof that the SAML token was in fact issued to that user.
1. A client requests a SAML token from a security token service, authenticating to that security token service by using Windows credentials.
2. The security token service issues a SAML token to the client. The SAML token is signed a certificate associated with the security token service and contains a proof key encrypted for the target service.
3. The client also receives a copy of the proof key. The client then presents the SAML token to the relying party and signs the message with that proof key.
4. The signature over the SAML token tells the party that the security token service issued the token. The message signature is created with the proof key for trusting party that the token was issued to the client.
Q.9 Describe some of SAML Authentication Protocols.
LDAP – Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
LDAP provides access to directory services, specifically X.500 based directory services. LDAP runs over TCP/IP connection oriented transfer services. LDAP offers communication language that applications use to communicate with other directory services.
Kerberos
Kerberos is a network authentication protocol. Kerberos is designed to provide strong authentication between client and server application by using secret key cryptography. It is an open standard. Commercial versions of this protocol is also there.
Oauth2
Oauth2 is an authorization framework that allows applications to provide limited access to user accounts on an HTTP service like Facebook, GitHub, and Digital Ocean.
SAML
SAML is an XML based language and is open standard. SAML exchanges authentication and authorization data between identity provider and a service provider. SAML was developed by the OASIS Security Services Technical Committee.
RADIUS
RADIUS stands for Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service. RADIUS is a protocol that provides centralized Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA or Triple A) management for users.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj