Table of Contents
Introduction to Cisco SD WAN Data Plane
vEdge is the component of Data plane. Data plane in any traditional network is responsible for moving packets from one location to another. This is commonly known as the forwarding plane. From a WAN perspective, common transports utilized to transmit data packets consist of the public Internet or private WANs (such as DMVPN, MPLS, or point-to-point connections). All of these technologies are built on some type of overlay for encapsulating and securing the data packets.
As wide area networks grow, the legacy transports start to have trouble scaling—particularly when securing the control and data planes. These functions consume a large amount of CPU cycles to process key exchanges and routing updates.
Cisco SD WAN Data Plane: Features
Features of data plane WAN edge are:
- WAN edge router of the site.
- Leverages traditional routing protocols like OSPF, BGP.
- Applies policies on data plane traffic.
- Establishes control plane (OMP) peering with vSmart.
- Provides secure data plane.
- Either hardware devices or software VNF support.
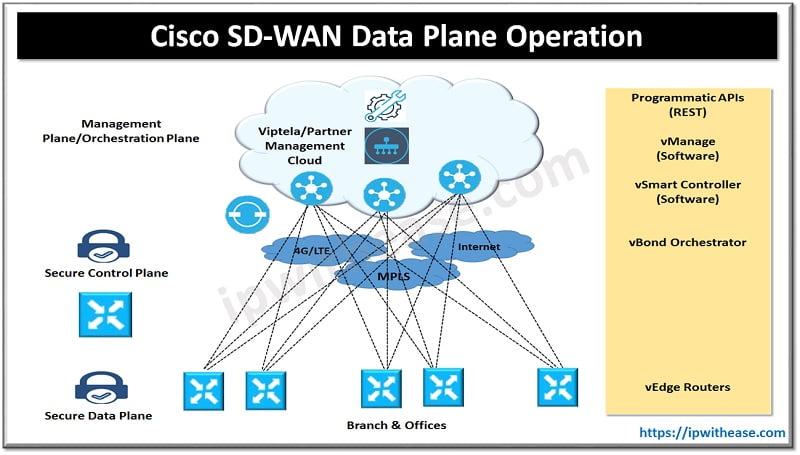
The Cisco SD-WAN solution is no different in that IPsec is used to secure the data plane. Traditional methods to provide segmentation across a WAN utilizing technologies such as MPLS L3VPN and DMVPN (MPLS over DMVPN) can be very complex and generally require more seasoned network engineers to implement, operate, and troubleshoot.
In the Cisco SD-WAN solution, segmentation is natively implemented and doesn’t require advanced experience to implement and support. Network segmentation also allows for different topologies per network segment. Cisco SD-WAN solution implements data plane routing, encryption, authentication, and segmentation.
TLOC Colors
TLOC is an OMP route type that provides reachability information to the WAN Edges on how to build the data plane to the rest of the WAN Edges in the network. TLOCs are what identify the WAN Edge to the physical underlay. A key attribute to TLOCs is their color. Colors are utilized to mark or categorize a specific transport. The network administrator will assign transports their respective colors when provisioning the routers. For example, all sites that have the same type of Internet circuit might use the same color. Policies can then be defined that control how data traffic flows across the overlay between these colors.
Currently, there are 22 pre-built colors broken into two categories (public and private). The color selected signifies when NAT is in play. Private colors are only to be used when there is no NAT between devices on the overlay. If there is a NAT device between WAN Edge devices, then use a public color.
TLOC Colors by Category
Public Color(s) | Private Color(s) |
3g | metro-ethernet |
biz-internet | Mpls |
public-internet | private1 |
Lte | private2 |
Blue | private3 |
bronze | Private4 |
| custom1 | private5 |
custom2 | private6 |
custom3 | |
gold | |
green | |
Red | |
silver |
If there is no color defined, then default is the color that will be advertised with the TLOC route.
Tunnel Groups
In this case, restriction is configured on the two transports. When these devices establish their control plane connections, they will advertise two TLOCs each: one for the public-internet color and another for the biz-internet color. Both of these routers will learn these TLOC routes and begin to establish data plane connectivity. Since restrict is configured, these routers will only build connections across their like colors.
Another option to restrict data plane connectivity is using tunnel groups. Only tunnels with matching tunnel groups, or no tunnel group defined, will form data plane connectivity (independent of the color). It is recommended that, if using tunnel groups, all sites have tunnel groups defined. A common deployment for this is when a data center has two physical connections to the same MPLS provider but the branch sites only have one physical connection, though the design calls for building connectivity across both physical interfaces in the data center.
Tunnel groups can be utilized with the restrict attribute as well. The rules of the two still follow, with restrict and color taking precedence. This means that if restrict is set on a color, and a tunnel group set, the router will only build IPsec tunnels between routers with not only the same color, but also the same tunnel group ID (or no tunnel group ID).
Conclusion
Data plane is responsible for distributed data forwarding function is known as Data Plane and its operation.
Continue Reading:
SD-WAN Control Plane Operation
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj