Over the last couple of years, a Virtual Private Network (VPN) has become a data security staple — for homes and businesses alike.
A VPN is an essential tool for people who connect to less secure public WiFi, want to stream content from other geographical regions, hide their location, and more.
With the rise in its popularity, customers are getting more and more VPN vendors to choose from.
To secure remote access for the workforce and protect their data, companies use a business VPN. Personal VPN packages cover all your individual needs at home.
But what is the difference between a personal and business VPN, exactly?
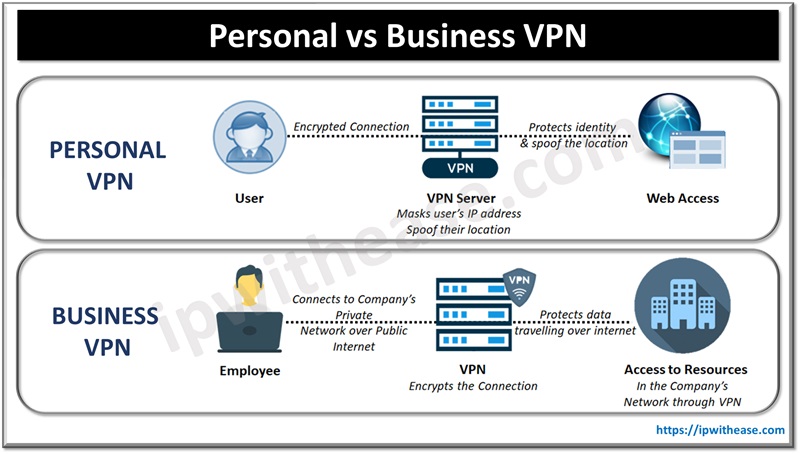
Similar Technology, Different Endpoints
The core Virtual Private Network technology is based on creating a safe (encrypted) tunnel that links two ends.
Personal VPN connects to the servers of their vendor. Servers are placed all over the globe, and all users share it. When they use a VPN, this new connection is safer, encrypted, and less likely to be intercepted by a malicious hacker. It also hides their location.
Business VPNs, on the other hand, connect to an internal network of a company or to reach corporate resources and databases. They enable safer access to the company’s internal infrastructure and assets for the workforce.
Organizations tend to choose either remote secure access or site-to-site VPNs. In the case of remote secure access, the technology is hosted at the endpoints of the company’s network — to secure access for remote workers.
Site-to-site type secures the connection between two corporate networks in different geographical areas.
Regardless of the exact type of VPN, the technology will include tunneling, strict authentication methods, and high-grade encryption. The main prerequisite is for the data to pass safely from one point to another.
The Purpose of Corporate and Private VPNs
According to Statista, almost half of VPN users (43%) rely on it for security purposes. Then 26% of respondents said they use it for streaming, 12% for privacy, and 9% to access geo-blocked content.
In remote corporate environments, the main purpose of a VPN is to support the employees. The goal is to provide the workforce with safe access to the company’s network while working from home or traveling.
Therefore, VPNs for businesses are tailored for more complex data security needs — such as meeting industry compliance. Companies use VPNs as one layer of security for their data — it complements other solutions.
For personal use, individuals are more concerned with accessing content that isn’t available in their country and making their browsing safe when they connect to public WiFi.
Business VPNs Have More Features
VPN packages for both corporate and personal VPNs have a long list of features and benefits. How to tell if you need military-grade encryption or split tunneling?
Let’s take a look at the most common features of both private and business VPNs and why they matter.
The most common capabilities of business VPNs are:
- Management of accounts
- Capability of compliance and audit
- Advanced encryption (such as the AES-256) protocol
Business VPNs accommodate a larger number of users. Their remote access to the infrastructure can be removed, added, or limited to certain parts of the network restricted from a single account.
Organizations need greater control over their traffic and a more efficient way of auditing and tracking it.
Data has to both be protected with strong encryption and meet compliance relevant to your industry — especially if you share personally identifiable information.
VPNs designed for personal use will usually have:
- IP masking
- Encryption
- Bypassing Geo-Restrictions
Your IP address is masked or seemingly replaced with another — meaning yours is concealed to make you anonymous.
Your data is encrypted while you browse the net.
Bypassing Geo-Restrictions allows you to access content blocked in your region.
Since it has more features, this also means that business VPN packages are available at a higher price compared to personal VPNs, which are generally more affordable.
Both VPNs Have Limitations
You cannot argue VPNs are not useful, but they’re generally more privacy-oriented than a means for cybersecurity. No tool can promise you foolproof cybersecurity or even complete privacy.
Virtual Private Networks are great at hiding your location, helping you access content, bypassing censorship, or making safer ways for employees to connect to the remote network.
But having a VPN doesn’t mean that you or your organization are completely safe from hackers.
Companies don’t use VPNs as their end-all cybersecurity measure against hacking and potential data breaches. They have other solutions that keep them safe from various cyber threats.
Private VPNs can be slower because they don’t have the bandwidths of a business VPN. They’re usually meant for one user and multiple devices that a person connects to.
Also, there is a common misconception that a VPN makes you completely anonymous. Your activity and location are concealed to a certain extent, but a VPN cannot make you invisible.
For example, the website you visit might not recognize your real location, but it can still use browser fingerprinting to remember the specification of your device and recognize it the next time you visit.
Which VPN Do You Need?
In a nutshell, a business VPN is suited for the corporate needs of large and small companies, while a personal VPN has all the functionality an individual needs to browse the net safely at home.
The main differences between business and personal VPNs are the cost, the intended use, and to which endpoint the VPN connects.
The best option for you will depend on the way your company operates or why you need the VPN at home.
If you have a company working remotely and are concerned about the privacy and security of your data, a business VPN is an obvious choice.
As someone who uses public WiFi or wants to stream foreign geo-blocked Netflix shows, a personal VPN will do just fine.
Continue Reading:
Top 100 VPN Interview Questions
Types of Virtual Private Network (VPN) & its Protocol
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.